

https://www.pling.com/p/2142966/
Maybe not all that close, but it’s the best I can think of right now.
I think it has the general old school vibe, maybe you could tweak the colors to be a bit brighter like your example?
⭒˚。⋆ 𓆑 ⋆。𖦹


https://www.pling.com/p/2142966/
Maybe not all that close, but it’s the best I can think of right now.
I think it has the general old school vibe, maybe you could tweak the colors to be a bit brighter like your example?


https://x-plus.store/products/n150-netbook
I picked one of these up after it got some buzz the other week. Still waiting for delivery, though, will report back once I’ve had some hands-on time with it! Probably just going to do Arch.
In addition to this, or rather before, you can run pacman -D --asdeps package_name to mark a package as a dep. If it is no longer required by something else it will be removed with the above. This can be useful for things that are deps that you installed manually at some point for some reason.
Oh, that’s some amazing info, thanks!
I had noticed this might be a problem when I was setting something up and tried to install a dependency that was already on the system. It informed me it was being set to explicit and I wondered if it might lead to a situation like that.
EDIT: More information provided. I disagree with the upvoted comment implying you should leave your system alone because you might break something. You’re using Arch, and part of the reason to use Arch is understanding how you built and maintain your system. Understanding how to inspect your system and perform proper maintenance is a crucial part of that. Read and think carefully before taking any actions and make sure any important information is backed up before taking major actions. Without throwing too much further shade, I find it disappointing so many in the community would take that stance and discourage you from pursuing this further.
When I switched to Arch, I started a notebook in Obsidian with a bunch of different information in it, I have a section devoted to Maintenance. Here are a few things I’ve put in there:
Clean package cache with paccache: https://ostechnix.com/recommended-way-clean-package-cache-arch-linux/
Clean orphaned dependencies: sudo pacman -Rs $(pacman -Qtdq)
Additionally, you can run pacman -Qe to list the packages you yourself have explicitly installed with pacman, or pacman -Qdt to list the packages that are dependencies of other packages. Use pacman -Qm to list packages not found in the official repositories (i.e., things installed through yay). This will allow you to review packages you may have explicitly installed in the past for some reason, but now find you no longer need.
For yay, I’m unsure if I should be using -Yc, -Sc, or -Scc. If anyone has more info with that, I’d appreciate it.
For flatpak: flatpak uninstall --unused
And for journals: journalctl --vacuum-time 7days
That’s most of the “automatic” stuff, cruft that can be cleaned out with little to no consequence. Other than that, you’ll just have to manually review what you have on your system.
If anyone has other commands or comments on the ones I provided, I’d be happy to accept further advice here as well 😃


I appreciate him trying to drum up excitement for the terminal. A lot of people are afraid of it and I understand why, but you don’t need to know everything about it in order to benefit from it.
I wanted to post some Trackmania replays to Bluesky when they first rolled out video, but they only supported up to 50MB. I dreaded having to open kdenlive, figure out how to work the GUI and then also possibly have to do some terrible math to balance size and quality. Maybe this is easier than I expected, but I found this: https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/520597/how-to-reduce-the-size-of-a-video-to-a-target-size
ffmpeg_resize () {
file=$1
target_size_mb=$2 # target size in MB
target_size=$(( $target_size_mb * 1000 * 1000 * 8 )) # target size in bits
length=`ffprobe -v error -show_entries format=duration -of default=noprint_wrappers=1:nokey=1 "$file"`
length_round_up=$(( ${length%.*} + 1 ))
total_bitrate=$(( $target_size / $length_round_up ))
audio_bitrate=$(( 128 * 1000 )) # 128k bit rate
video_bitrate=$(( $total_bitrate - $audio_bitrate ))
ffmpeg -i "$file" -b:v $video_bitrate -maxrate:v $video_bitrate -bufsize:v $(( $target_size / 20 )) -b:a $audio_bitrate "${file}-${target_size_mb}mb.mp4"
}
ffmpeg_resize file1.mp4 25 # resize `file1.mp4` to 25 MB
ffmpeg_resize file2.mp4 64 # resize `file2.mp4` to 64 MB
I’m not proficient in bash enough to have written this myself, but even I can glance over this and see it’s just doing some math for me while invoking two programs: ffprobe and ffmpeg. Easy peasy.
I put this in my ~/.bashrc and use it all the time now, it’s almost silly how simple this has made things. I get why nerds get super attached to their profiles now, I’m collecting a bunch of scripts and functions that just make life easier.
Currently I’m working on writing some scripts with ratbagctl (https://github.com/libratbag/libratbag) so when I launch a game through Steam it’ll automatically set my Logitech mouse profile for that game. You know, the thing the Logitech mouse software makes you sign up for an account and connect to the internet for. All of the control, none of the bloat 😝
For those not in the know, “Trusted Computing” is a very specific THING and maybe not what you’d expect, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trusted_Computing
TC is controversial as the hardware is not only secured for its owner, but also against its owner, leading opponents of the technology like free software activist Richard Stallman to deride it as “treacherous computing”,[3][4] and certain scholarly articles to use scare quotes when referring to the technology.[5][6]
You can pretty much guess where I land.
a backup of your bitlocker key is in your Microsoft account, and normally nowhere else. It’s pretty easy for Microsoft to lock you out of your ow computer and data completely, if they wanted.
You make a good point, I’m missing the forest for the trees. Why even bother theorizing that BitLocker may be compromised when they’re removing local accounts for consumers and forcing the key to be uploaded to their servers anyway?
Yep! They don’t teach this stuff because consumer level cyber security is in the absolute pits of despair and moreover, they’re trying to do away with what little we have access to. Governments and police agencies like how easy it is to access files.
Personally I don’t bother with full disk encryption (FDE) since I don’t really have anything private on my main computer. Just a bunch of game files, comics, movies, etc. Anything extremely important such as tax documents, personal data, etc. is honestly very small and I keep in a little Proton Drive folder, <1GB total. I think the best approach is to simply educate yourself and be aware of what’s worth protecting and how best to protect that. Just enabling FDE and thinking you’re safe ignores all the other avenues that personal data can be stolen.
My current pet conspiracy theory is that FDE with BitLocker isn’t even worth it on Windows due to the TPM requirement. Why is that a bad thing? Your system probably has fTPM supported by the BIOS, why not just enable that?
Integrating with features like Secure Boot and Windows Hello for Business, TPM 2.0 enhances security by ensuring that only verified software is executed and protecting confidential details.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5283799 (I don’t believe we’ll see this EXACT implementation of DRM, I’m just providing an example of TPM being used for DRM and that these ideas have been in consideration since at least 2009).
Now, if I were Microsoft and I wanted to exert an excessive amount of control over your system by making sure you couldn’t run any inauthentic or “pirated” software to bring it more inline with the walled garden Apple approach they’ve been salivating over for the past decade+, you’d first need to ensure you had a good baseline enabled. You know, kind of like the thing you’d do by forcing everyone into an OS upgrade and trashing a lot of old hardware.
It won’t be instantaneous, I don’t know exactly how or what it’s going to look like when they start tightening their grip. Again, this is all speculation, but it’s not hard to connect the dots and their behavior over the past couple years does not give them the benefit of the doubt. Microsoft is no longer a company that can be assumed to be acting in the best interest of the average consumer, they’re not doing this for your security. They want to know that your computer is a “trusted platform”.
EDIT: Further lunatic conspiracy theories: BitLocker is/will be backdoored so Microsoft forcing you into that ecosystem further guarantees they have access to your system. This all stinks to me, like your landlord telling you how you can arrange the furniture in your own apartment.
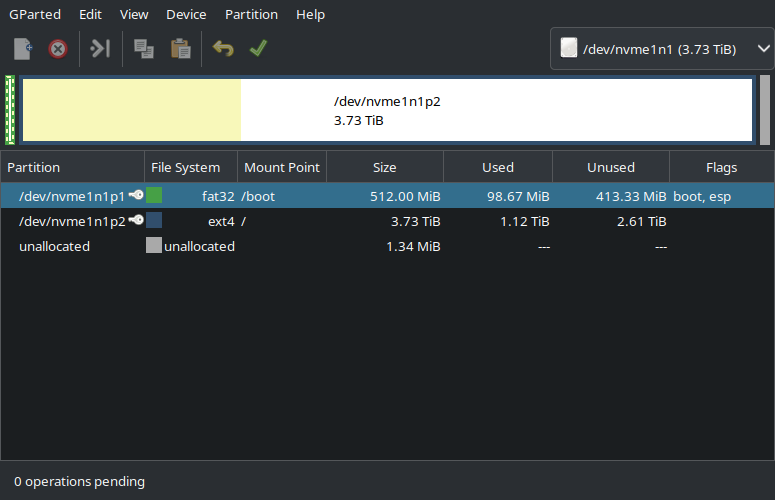
Just used the default for one big partition. I used to do tedious partition configurations, but it always ended up biting me down the road more than helping. This drive is for the OS, games, and working files. I have a 16TB NAS that holds anything worth saving, so if I need to nuke the whole thing and do a reinstall, all I really end up doing is downloading a bunch of Steam games again.
I use Arch on all my systems now. It does great for gaming on both my beefy gaming PC and my little work laptop (within their respective punching weights). I haven’t felt the need to explore CachyOS or any other variants for performance gains and I really do appreciate how bare bones Arch is. Just having the lightweight OS that isn’t doing a darn thing beyond what I’ve asked it to claws back plenty of performance, although I’m speaking more in contrast to Windows than other distros having any sort of bloat.
Still, Arch has been the first distro I really committed to, I’ve been on it for a year and a half now and learning how to build it out taught me a lot about Linux.
Also, I’m just never sure how long some of this offshoot distros will hold on for, you know? Is that unfounded?
Protontricks can help for some games. Personally I used it to install Openplanet for Trackmania which doesn’t have any sort of explicit Linux support specified.
What Protontricks does is allow you to run installation files within the context of a steam game, as you mentioned. Simply launch Protontricks and select the game you’re trying to modify and it will mount it properly for you. Then choose “Run an arbitrary executable (.exe/.msi/.msu)” and proceed to run the installer as you would normally.
Sometimes the path can still be a bit janky. For example when Openplanet wanted to install to the Trackmania directory as mounted through Protontricks, I had to specify: Z:\home<USERNAME>.steam\steam\steamapps\common\Trackmania.